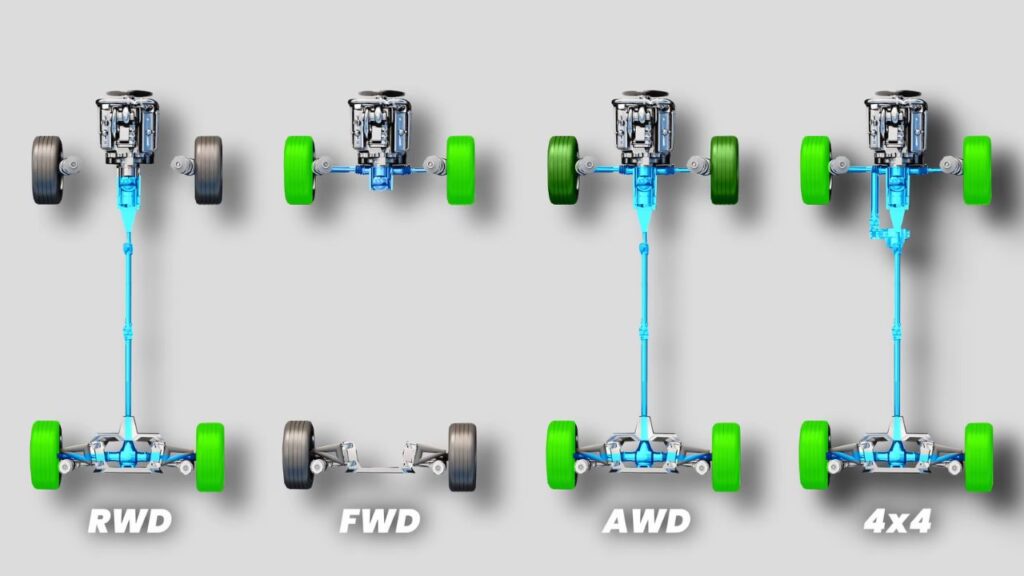
You might have heard of different types of drivetrains, but do you really know what FWD, RWD, AWD, and 4×4 mean? Probably not, right? Well, don’t worry! Our team has put together this post to break it down for you and help you decide which one best suits your needs.
What is a drivetrain differential?
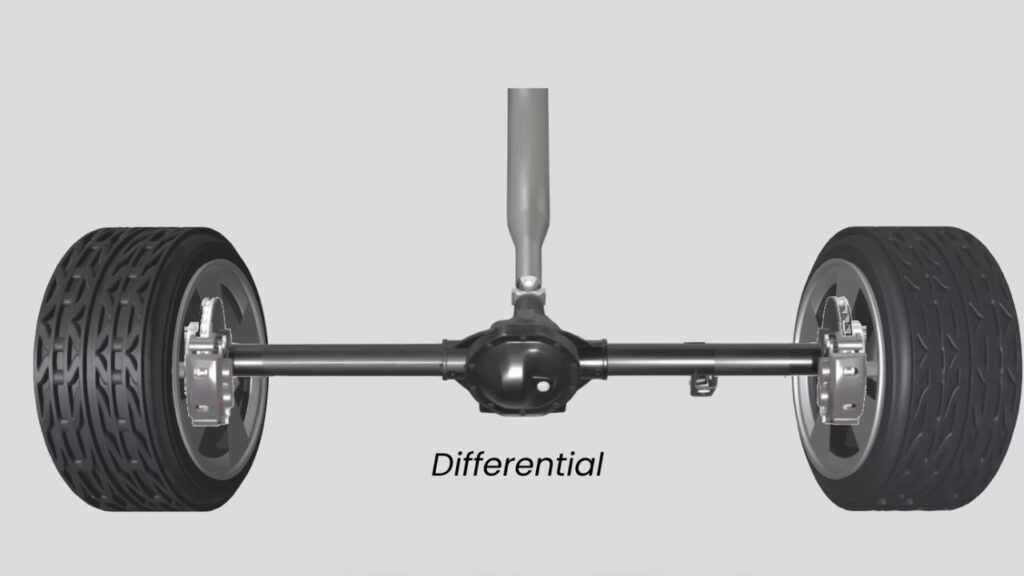
Before diving into specific drivetrain types, let’s understand a crucial component that makes modern driving possible: the differential. Think of it as the unsung hero of smooth driving.
When you’re driving straight, both wheels on an axle rotate at the same speed. But what happens when you turn? The outer wheel needs to travel a longer distance than the inner wheel. Without a differential, your car would hop and skip through turns, making handling difficult and potentially dangerous.
This is where the differential comes in. it’s and mechanical device that facilitate wheels to rotate at different speeds while still delivering power to both. I contains series of gears which work together to distribute power effectively, ensuring smooth handling in sharp turn or cruising straight ahead.
Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD)
You probably have heard people praise rear-wheel drive vehicles for their “perfect balance” and “pure driving experience.” But what makes RWD special?
In a rear-wheel drive system, power generated from engine is transferred from transmission and down a long driveshaft to the rear wheels. This setup creates a natural weight distribution that performance drivers love. In this system when you accelerate car’s weight is shifted to back, which gives more traction to the driving wheels.
The main advantage? it offers better handling and acceleration in high-performance vehicles. However, this drivetrain underperform in slippery conditions like snow or rain, where front-wheel drive outshines AWD.
Front-Wheel Drive (FWD)
Lets talk about modern day drivetrain front-wheel drive, FWD systems are efficient, cost-effective, and provide good traction in most conditions. In this system, weight is shifted on driving wheels, which helps in snow or rain weather by providing higher level of traction.
Front-Wheel Drive has a unit called transaxle which contains engine and transmission together. you must have noticed more space in FWD vehicles which is because of placement of drivetrain. Highlighted features are reliability, efficiency and daily transportation.
Four-Wheel Drive (4×4)
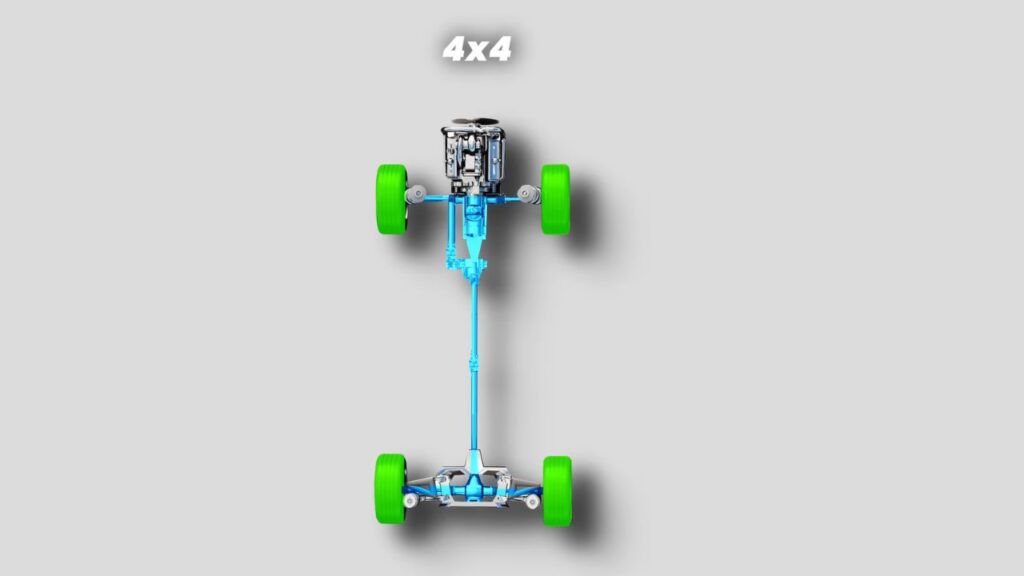

4×4 system is designed to handle different conditions like snowy rides to off-roading:
- 2H (Two-High): For normal road driving
- 4H (Four-High): For slippery conditions at normal speeds
- 4L (Four-Low): For serious off-road challenges
The magic happens in the transfer case, which can split power between front and rear axles. When you engage 4L, the system multiplies torque significantly – imagine having four times the climbing power.
All-Wheel Drive (AWD)
Think of AWD as the tech-savvy cousin of 4×4 systems. Rather than requiring driver input to change modes, AWD systems automatically adjust power distribution based on conditions. Using sophisticated sensors and computers, these systems can detect wheel slip and redirect power in milliseconds.
Modern AWD systems are perfect for drivers who want all-weather capability without having to think about engaging different modes. While they might not match the extreme off-road capability of proper 4×4 systems, they offer excellent performance in most real-world conditions.
Our Final Thoughts
Modern drivetrain technology has come a long way, offering solutions for every driving scenario imaginable. Whether you’re seeking performance, practicality, or off-road capability, there’s a drivetrain system designed to meet your needs. i hope this guide has helped you to understand all types of drivetrains.
